EHR Interface Design Principles, UX, And Usability Challenges
EHRs store and manage patients’ health data, improving healthcare-provider communication. As they become increasingly prevalent in healthcare, it is essential to prioritize interface design principles that enhance user experience (UX) and usability since poor interfaces can slow the process and frustrate users.
This blog post will discuss EHR interface design principles, UX, and usability issues, as well as ways to improve user experience. Also, we can maximize EHR benefits for providers and patients by understanding and overcoming healthcare providers’ EHR design challenges.
What Is EHR Design?
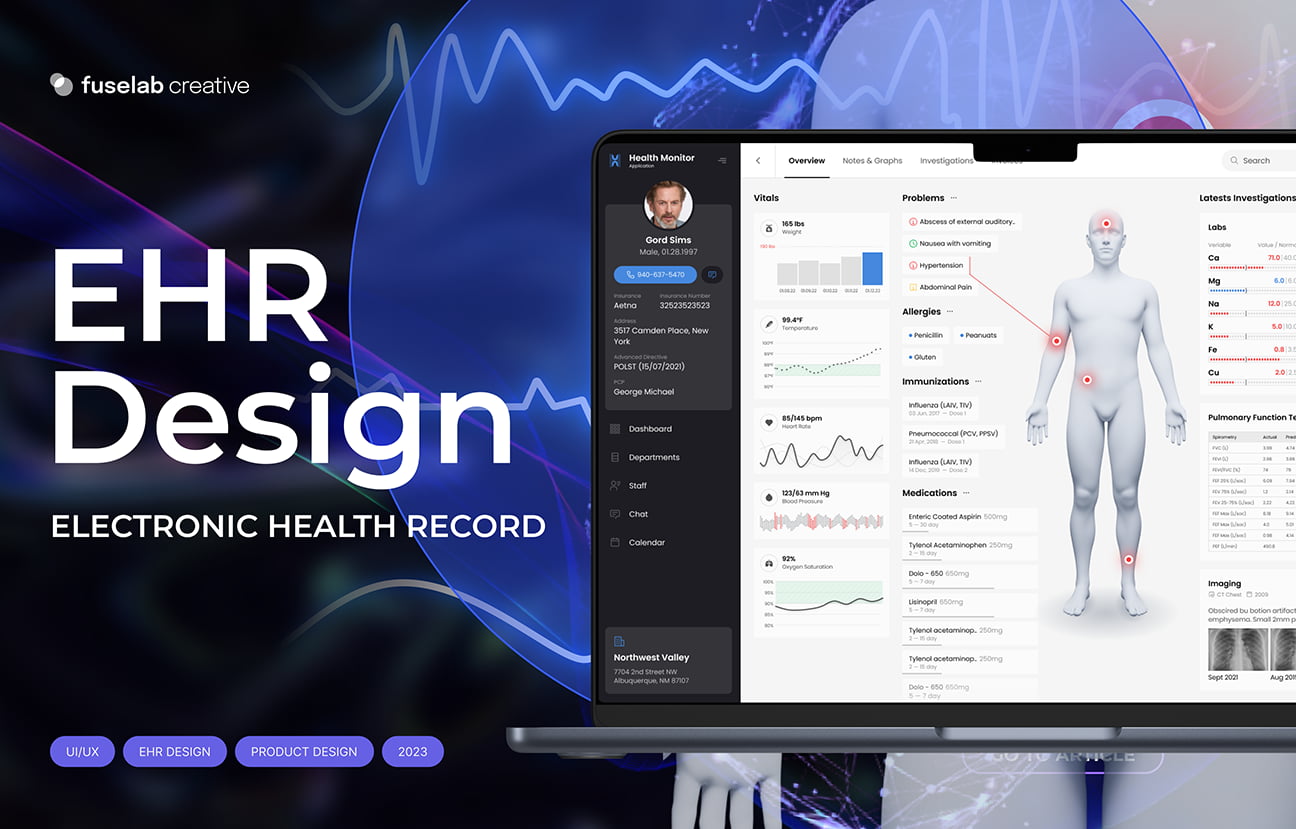
EHR design allows healthcare providers to securely store, manage, and share patient data. EHRs have made real-time patient data analysis easier for doctors. Moreover, an EHR dashboard offers a user-friendly and extensive overview of the patient’s health information and facilitates efficient navigation through the EHR system, making it an essential part of the EHR interface.
As of 2021, 78% of office-based physicians and 96% of non-federal acute care hospitals had certified EHRs. The adoption of EHRs has increased significantly since 2011, with 28% of health facilities and 34% of physicians now using them.
Intuitive EHR design not only enhances EHR user experience but also significantly improves patient outcomes by enhancing patient safety, creating greater healthcare efficiency, and reducing medical errors. Conversely, poorly designed EHRs can confuse, slow medical providers down, and potentially result in harm.
Hence, EHR designers must consider several factors, such as:
- User interface design: Healthcare professionals use EHR systems primarily through the user interface. User interface design should, at the very least, be intuitive, simple, and efficient.
- Data Visualization: EHRs should display patient data in whatever fashion is most expedient for users to digest easily and quickly. Designers should create custom color coding, interactive graphs, and medical charts to help healthcare providers quickly identify important information over less important through design, simple clicks, and/or hovers. And for those deploying tablet formats, designers need to be well-versed in touch and multi-touch navigation to make the greatest use of the applied technology.
- Interoperability: Ideally EHRs should share patient data with other healthcare systems, as this is the only way to truly put the patient’s health first. Obviously, in multi-provider cases, this is crucial. And, yes, we know that this is not a design point we are making, but we are including it here because we are in the business of helping in the care of patients as a whole and this is an important issue that comes up in discussions with the medical community all the time.
- Security and privacy: EHRs must safeguard patient data; which means, designers must consider encryption, user authentication, and access controls within everything they design.
Simple Interfaces and Intuitive Workflows
Many healthcare organizations use Epic, Cerner, and other widely recognized industry platforms. These systems have simple interfaces and intuitive workflows, and some have fairly powerful data visualization features. However, they often fall short in their attempt to be all things to all audiences when it comes to intuitive design approaches. Intuitive user interface design services focus on creating interfaces that meet the needs of users from all walks of life and level of technical savvy, while at the same time meeting the business goals of the system itself. This is no easy task and is something that is constantly changing and evolving as AI and other types of advancement are added to the medical IT lexicon.
Poorly designed EHRs can cause errors and adverse events. According to the Pew Charitable Trusts, nearly one-third of physicians said EHRs had caused medical errors. Now this is not always a technology-caused error, there are so many factors that play a role in medical errors, which is why one of the number one costs for any large medical system is insurance. But let’s focus on the positive side of things for now.
Lastly, EHR design is now an essential pillar in the world of safe and effective healthcare and most thought leaders in our space agree that to improve patient outcomes EHR designers must finely tune their knowledge and skill with everything we have discussed up to this point before taking on a project involving enterprise UI design, medical data visualization, EHR dashboard design, or medical IT software development in general.
Understanding Electronic Health Record System Design
EHR system design allows healthcare providers to securely document, manage, and share patient data. EHR system design ensures that healthcare providers can quickly and efficiently access information, which has been proven to improve patient outcomes.
Moreover, medical dashboard design provides healthcare professionals with a centralized location for real-time monitoring of patient data and analytics. Imagine you are an ER doctor, and you are forced to make a life-and-death decision based on a bunch of old paper medical records a family member brought with them to give you. This was a daily occurrence not that long ago. But now with EHRs and interactive digital design, the healthcare community has a treasure trove of life-saving tools at their fingertips. This is only one reason in a long list of reasons that we love working on behalf of medical providers across the world.
EHR system design best practices include:
- User-Centered Design: Designers must consider that most providers have almost no extra time to spend learning a new software system, and that just like mobile apps, everything needs to be immediately usable and intuitive.
- Interoperability: EHRs should be designed for healthcare system interoperability. Understand standard medical data formats and coding systems well before beginning your work.
- Test and Iterate: EHR system designers should test and iterate system design as often as possible during their work progress. User testing helps identify system improvements early and saves time and money by not having to make costly changes during code development.
- Follow Industry Standards: Design EHR systems using industry standards for coding, interoperability, terminology, abbreviations, and universal iconography where possible.
EHR Design Importance: Improving Healthcare Delivery with EHR UX/UI Design
EHR system design is essential to healthcare delivery. EHR system design can improve patient outcomes, reduce medical errors, and streamline healthcare delivery. Healthcare app design involves creating user-friendly and secure applications that meet the unique needs of healthcare organizations while improving patient care and outcomes.
Why EHR Design is Important:
EHR design matters for several reasons:
- Better Efficiency: Well-designed EHRs help healthcare providers manage patient data efficiently. EHR systems streamline workflows, automate processes, and reduce administrative burdens, allowing healthcare providers to spend more time with patients.
- Enhanced Patient Safety: Effective EHR design reduces medical errors, improving patient safety. EHR systems give healthcare providers real-time access to patient data, preventing medication errors, drug interactions, and patient safety issues.
- Better Communication: EHR systems improve healthcare provider communication, improving care coordination and patient outcomes. Interoperable EHRs allow healthcare providers to share patient data across settings, improving care transitions.
Additionally, EHR design enhances healthcare delivery. EHR systems improve patient care by making patient data easy to access. Lastly, it enhances healthcare by:
- Patient Engagement: EHR systems give patients access to their health data, empowering them to participate in their care.
- Improving Care Coordination: EHR systems enable healthcare providers to easily share patient data. This improves care transitions and patient outcomes.
The Impact Of EHR UX Design On Patient Care:
EHRs designed for healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes by:
- Improving Treatment Planning: EHR systems give healthcare providers a complete picture of a patient’s health, including medical history, medications, and lab results. For instance, if a patient has a complicated medical history and takes multiple medications, the EHR system can provide a broad analysis of their health status to help the provider develop a treatment plan.
- Improving Patient Safety: EHR systems can alert healthcare providers to potential safety issues. E.g., Clinical Decision Support (CDS) tools alert healthcare providers to possible medication interactions and allergies. If a patient has a registered allergy to a medication, the EHR system can alert the provider when they try to prescribe it, preventing a severe adverse reaction.
In conclusion, effective EHR functional design is crucial in improving healthcare delivery, enhancing patient safety, and reducing medical errors by meeting the needs of healthcare providers and patients through thoughtful consideration of user interface design, healthcare data visualization, interoperability, security, and privacy.
EHR Design Principles: 14 Core Principles Of User-Friendly EMR System Interface
A set of 14 usability principles for creating EMR app interfaces was established by the American Medical Informatics Association. They are widely utilized to gain a better understanding of how to improve the user-friendliness of EHRs and EMRs.
- Consistency
The overall look and feel of the EMR interface should be consistent with the rest of the system. Data exchange standards, such as HL7 practices, must also be adhered to. - Visibility
All data displayed in an EHR user interface must be legible and easily understood by users. You should also consolidate where possible to make the most critical data easily accessible and relevant. - Match
The interface of an electronic health record system should be consistent with the userbr>actual setting. For instance, digital drug charts must have the same fields as paper ones. - Minimalism
Simplify the process so users can accomplish their goals with as few clicks as possible. Limit yourself to only the most important reminders and alerts. It allows doctors to spend less time on administrative tasks and more time with patients. - Memory
Ease the mental strain on the user by recalling previously entered data, switching tobr>checkbox for data entry, emphasizing key information, etc. - Feedback
Provide users with immediate feedback as they take various actions. Breadcrumbs can help guide users through your site, while pop-up windows and in-text links can provide additional context or instructions, respectively. - Flexibility
Give people the tools to make the EHR work the way they want it, which helps providers save time. Allow them the freedom to set preferences, create shortcuts, use voice commands, and switch options on and off.
- Message
When users make a mistake, provide them with clear error messages to help them fix the issue. Each notification needs to specify what went wrong, as well as how to fix it. - Error
Eliminate human error from data entry and other sources by having the input checkbr>mechanically. For example, one way to improve usability is to restrict text entry in fields where only numerical data is required. - Closure
Let people know when they’ve finished a task and show them how many there were in total. A green checkmark or a confirmation window can be displayed to indicate success. - Reversibility
Create a user-friendly EHR interface with features like undo, redo, and saving drafts of work before publishing to a broader medical user base. - Language
Improve readability and uniformity of textual elements for better user comprehension. You must also use standard phrases and language. - Control
Users need to feel in complete command while interacting with your systems. All outcomes, messages, and data displayed need to be immediately understandable and not require research or deciphering. - Documentation
When an EHR interface calls for a complex action that might not be immediately apparent to the user, extra guidance should always be provided.
Common EHR Usability Challenges
EHR usability is how easily a healthcare provider can use and understand an EHR system. It impacts healthcare efficiency and accuracy. An easy-to-use EHR system should support healthcare providers’ workflows, data entry, and retrieval. Moreover, EHR usability testing can identify areas for improvement, like healthcare provider satisfaction, user errors, and patient outcomes.
Usually, providers use the System Usability Scale (SUS) to evaluate EHR usability. SUS is not a traditional ranking system. Instead, it collects ten statements about EHR UX within the system and provides a general ranking.
Despite the benefits of electronic health records (EHRs), healthcare providers face various challenges related to the usability of EHR, which can impact the quality of patient care and provider satisfaction. In other words, investing in the wrong EHR can only be extremely costly and time-consuming for staff, it can also adversely impact patients.
1. An Inconvenient Interface
Healthcare providers often struggle with a complicated EHR interface. EHR UI design affects usability and efficiency. Also, healthcare providers can become frustrated and make mistakes with a cluttered interface with too many options.
A complicated interface slows data entry and retrieval, reducing healthcare delivery efficiency. Healthcare providers may spend a lot of time navigating the interface, searching for patient data, and entering new data, which takes away patient time.
Hence, to reduce cognitive load and improve efficiency, EHR designers should prioritize user interface simplification, and please, please, please do extensive user testing and re-testing to certify its usability.
2. Data Entry Issues
Healthcare providers also need help with EHR data entry. EHR systems require precise data entry, which takes time. As a result, data entry issues by healthcare providers may lead to errors and incomplete data, which can delay or result in the misdiagnosis of patients.
Moreover, data entry errors can result from unclear labeling or workflows. Hence, EHR designers should simplify the process to address these issues. They can use intuitive labeling, clear instructions, and validation checks to ensure data accuracy. Voice recognition and NLP can also speed up data entry.
3. Insufficient workflow support
The specifics of a clinical setting, such as the interactions and workflows that would make the system truly efficient, are often overlooked when an EHR product is developed and implemented in isolation. As a result, adoption lags, and employee burnout might rise. It’s also possible that doctors will find ways around using EHRs.
Unfortunately, patients may also be harmed by the lack of workflow support. The lack of usability in EHR can also have negative consequences for patients, such as increased stress levels. The Pew Charitable Trusts highlighted an alarming incident in their review of pediatric care, in which the ordering of an emergency blood transfusion for a newborn was delayed because the clinicians needed the Apgar Score first, which they were unable to obtain in time. In the end, the child did not receive treatment promptly because of how the EHR workflow was designed.
Overcoming Usability Challenges In EHR Design
EHR usability issues can affect patient care and outcomes. Here are some important EHR usability principles and strategies:
Conduct Usability Testing: Usability testing helps improve your poor EHR design. Usability testing with healthcare providers throughout the design process ensures that the system is easy to use and meets their needs.
Involve Healthcare Providers in the Design Process: Healthcare providers can help design the EHR system to meet their needs and workflows. Healthcare providers can evaluate system usability and suggest improvements.
Prioritize User Interface Design: EHR usability depends on user interface design. Simplifying, labeling, and optimizing the user interface should be designers’ top priorities. For instance, Meditech and NextGen have used user-centered design and extensive usability testing to improve their EHRs’ usability.
In conclusion, EHR usability issues must be addressed to improve healthcare efficiency and effectiveness. Designers can create EHR systems that meet healthcare providers’ needs and improve patient outcomes by involving users, prioritizing user-centered design, usability testing, and user training.
Best Practices For EHR User Interface Design
User interface design improves EHR usability and efficiency. EHR interface design best practices:
- Simplify the User Interface: A cluttered interface is overwhelming and inefficient. Hence, EHR designers should eliminate clutter and prioritize key features to simplify the user interface and build around a distinct hierarchy of patient data.
- Use Clear and Consistent Labeling: EHR systems should avoid confusion and errors by labeling clearly. Designers should use standard terminology and label clarity to provide users the ability to scan and pinpoint areas of concern or interest to the provider.
- Design for Efficiency: EHRs should support efficient workflows. Healthcare providers’ workflows should inform system design. For instance, frequently used features should be easily accessible within a few clicks.
- Use Meaningful Data Visualization: EHR systems should display patient data. EHR data visualization helps doctors quickly identify and interpret patient data without having to read pages of information. EHR graphic design, color coding, and charts help designers communicate information.
According to the National Library Of Medicine, 96% of healthcare providers choose an EHR system based on usability. Hence, those who follow EHR user interface design best practices can improve efficiency, accuracy, and patient outcomes, while also increasing sales.

Final Thoughts!
In conclusion, complicated interfaces, data entry issues, and insufficient workflow support can affect patient care and provider satisfaction.
To address these challenges, designers need to prioritize user-centered design, usability testing, training, and clear labeling while engaging healthcare providers in the design process.
Ready to take your healthcare UI/UX design to the next level? Look no further than Fuselab Healthcare UI/UX design agency. Our team of experts specializes in creating user-centered design solutions that enhance the patient experience.
With a focus on user interface, data visualization, interoperability, security, and privacy, we’re committed to improving healthcare delivery, and patient safety and reducing medical errors. Contact us today to take the first step toward high-quality patient care.